“Right Coronary Artery Blockage: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options”
-
- Dr. Junaid Arshad
- March 12, 2022
- 0 comments
Table of Contents
“Right Coronary Artery Blockage: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options”
What happens when the right coronary artery is blocked?
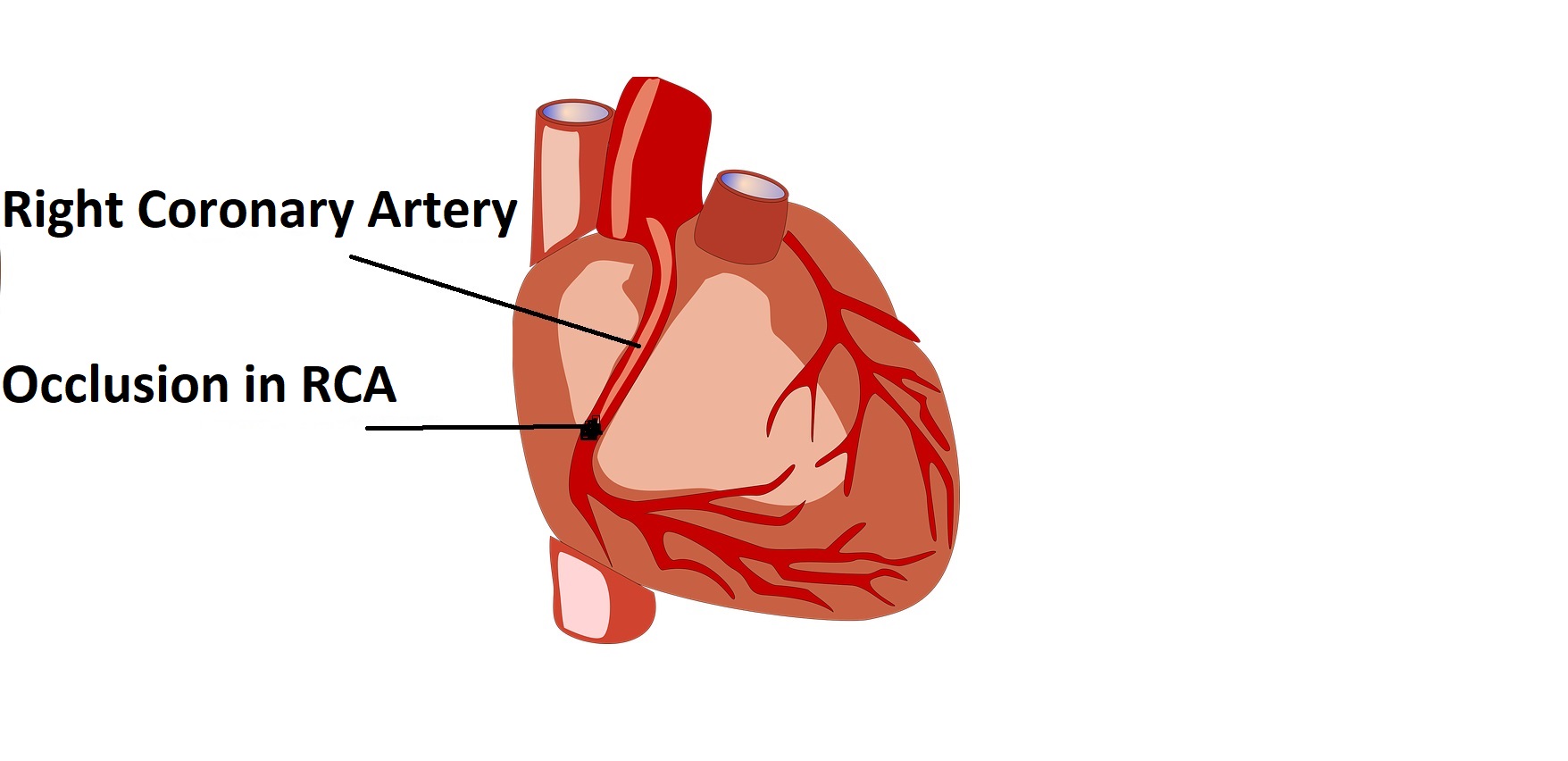
The right coronary artery (RCA) is one of the major blood vessels supplying blood and nutrition to the heart and its occlusion can cause a heart attack predominantly affecting the inferior surface of the left ventricle, the right ventricle & the right atrium. It also supplies blood to the SA node & AV node which constitute the conduction system of the heart The lack of blood supply to the conduction system may result in the development of bradycardia(slow heart rate) & heart block. Right ventricular involvement and heart block are the two serious complications of a heart attack caused by RCA occlusion.
RCA blockage causing Inferior wall Myocardial Infarct(Heart attack)
RCA supplies…
Statistics say that 40% of heart attacks involve the inferior wall.
RCA supplies blood to the inferior region of the heart in patients with right dominant circulation. In the right dominant circulation, a branch called PDA(posterior descending artery) arises from RCA. This is present in 80% of the population.
In 20% of the population, PDA arises from the left circumflex artery(LCx) and is called the left dominant circulation. In these patients, the inferior region of the heart is supplied by the LCx artery.
The manifestations of RCA occlusion depend upon the degree of occlusion.
Patients who have 50% or less occlusion may remain completely asymptomatic.
Those who have 70% occlusion may experience anginal pain. Anginal pain is the chest pain that occurs with physical activity like walking, running, & climbing stairs. It lasts for around 10 minutes and settles with rest. This type of angina is called stable angina.
As the narrowing in the blood vessel progresses, the anginal pain may worsen and occur at rest. This is called unstable angina.
When the right coronary artery is 100% occluded it causes a heart attack called ST-elevation myocardial infarct (STEMI).
Patient experiences severe chest pain which is diffuse and may be referred to the left arm and jaw.
Sweating & apprehension may also occur.
Any patient experiencing such symptoms should immediately report to a cardiac emergency.
RCA blockage causing Bradycardia and Heart Blocks
Bradycardia(slow heart rate) and heart block are the common & well-recognized complications of inferior wall MI and RCA blockage.
Slow heart rate is the most common rhythm abnormality and it may be completely asymptomatic.
Heart blocks can be life-threatening if not detected and treated promptly.
The conduction system of heart
For understanding heart blocks, basic knowledge of the conduction system is necessary which is given below.
The conduction system of the heart is made up of specialized cells that generate an electrical impulse.
The electrical impulse travels in a sequential manner through the conduction system to cause a well-coordinated contraction of the chambers of the heart i.e atria and the ventricles.
Any abnormality in the electrical impulse can break up the coordination between the atria and the ventricles and they may start to beat independently, which in medical terminology is called heart block.
Mentioned below are the parts of the conduction system as per the sequence of an electrical impulse.
# 1. SA Node
SA node or sinoatrial node is a part where electrical impulse starts.
It is also called the pacemaker of the heart.
It receives blood supply from RCA in 60% of the patients & from LCx in 40% of the patients.
So RCA blockage affects the generation of electrical impulse from the SA node and may result in bradycardia.
#2. AV Node
AV node or atrioventricular node receives an impulse from the SA node.
It is supplied by RCA in 90% of the population, by a branch called AV nodal branch.
The remaining 10% population receives blood supply to the AV node through the LCx artery.
#3. Bundle of His
After the AV node, the electrical impulse reaches the bundle of His.
The bundle of his is supplied by the AV nodal branch of RCA. It also receives minor blood supply from LAD(left anterior descending artery).
#4. Right and left bundle branches
The bundle of His then divides into right and left bundle branches.
Both right and left bundle branches receive most of their blood supply from LAD, may also receive some collaterals from RCA and LCx.
#5. Purkinje fibers
The bundle branches then give off the Purkinje fibers that ultimately enter both right and left ventricles.
Importance of RCA for conduction system
The above-mentioned information makes it clear that the conduction system receives a major part of the blood supply from RCA.
This is the reason that RCA blockage is associated with abnormalities in the generation and propagation of electrical impulse which is manifested in the form of heart blocks.
How common are heart blocks with RCA blockage?
Sinus bradycardia(slow heart rate) may occur in 40% of the patients in the first 2 hours.
Another study showed that complete heart block occurs in 9.4% of patients with inferior wall MI.
Treatment of heart block with RCA blockage
The treatment of patients who develop heart block after RCA blockage and inferior wall MI depends on hemodynamic stability.
Hemodynamicaly Unstable patients
Hemodynamically unstable patients having bradycardia & blood pressure of less than 90/60 mmHg should be immediately treated with atropine and temporary pacing.
Signs and symptoms of hemodynamic instability include low blood pressure, altered consciousness level, and heart failure leading to acute pulmonary edema.
A temporary pacemaker is inserted through veins like the femoral, subclavian, or internal jugular vein. The procedure should preferably be carried out under fluoroscopy but can be carried out at the bedside in an emergency, in case a fluoroscope isn’t available.
Revascularization of the blocked RCA with either fibrinolysis or PCI may correct the heart block.
If the block persists, a permanent pacemaker should be considered.
Hemodynamically Stable paients
Hemodynamically stable patients do not require atropine or temporary pacing.
But such patients should be very closely monitored as they can become unstable.
Prompt revascularization with either PCI or fibrinolysis(if PCI is not available) should be done.
Reopening of blocked RCA usually corrects the heart block in such patients.
Right Ventricular Infarct
Heart attack involving the right ventricle is another complication of RCA blockage/inferior wall MI.
It occurs in 30-50% of patients with inferior wall MI.
Also, it is associated with poor outcomes and increased in-hospital mortality.
Sign and symptoms of RV infarct
Symptoms of RV infarct include.
- Chest Pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Anxiety
Shortness of breath is not a symptom of isolated or predominant RV infarct.
Signs of RV infarct include low blood pressure(hypotension) & elevated jugular venous pulse.
How RV infarct is diagnosed
ECG
ECG with right-sided leads should be obtained in patients with suspected RV infarct.
ST-elevation of 1mm or more in leads V4R, V5R, and V6R is diagnostic of RV infarct.
ST-elevation specifically V4R has a sensitivity of 88% for the diagnosis of RV infarct and it indicates occlusion of proximal RCA.
Echocardiography
Echocardiography shows regional wall motion abnormality in the right ventricular region(hypokinesia, akinesia, dyskinesia).
It may also show decreased RV ejection fraction.
Right coronary artery blockage treatment
- Primary PCI or fibrinolytic therapy for the revascularization of the blocked RCA is the treatment of choice.
- As already mentioned above, the patients with heart block and hemodynamic instability should be managed with IV atropine and temporary pacemaker.
- Management of patients with hypotension and RV infarct is complex. IV fluids and inotropic agents are used.
- Pain control should be done with opiods.
- Beta blockers should be avoided in RV infarcts as they can decrease heart rate & blood pressure and also slow the AV conduction.
How serious is right coronary artery blockage?
The outcomes of RCA blockage depend upon the development of complications like heart block and right ventricular infarction. Both of these complications are associated with worse outcomes and increased in-hospital mortality. However, in the era of fibrinolysis and primary PCI, the outcomes have improved.
A study has shown that in-hospital mortality is doubled in patients who develop complete heart block, even in the era of PCI.
Another study showed that patients with AV block, treated with thrombolysis after inferior wall MI, have an increased mortality of 15% in the first 30 days as compared to those without AV block.